Anti counterfeiting technology companies – Anti-counterfeiting technology companies are playing an increasingly crucial role in protecting businesses and consumers from the devastating effects of counterfeiting. This pervasive issue impacts various sectors, from luxury goods and pharmaceuticals to food and beverages, leading to significant financial losses and safety risks. This exploration delves into the market landscape, technological advancements, and challenges faced by these companies, highlighting their importance in safeguarding global commerce and public health.
The fight against counterfeiting is a complex battle fought on multiple fronts, requiring innovative technological solutions and robust legal frameworks. This analysis examines the diverse technologies employed, including blockchain, AI, RFID, and digital watermarking, and assesses their effectiveness in various industries. We’ll also consider the challenges in widespread adoption, such as cost, implementation complexity, and regulatory hurdles, and explore potential solutions to overcome these obstacles.
Market Landscape of Anti-Counterfeiting Technology Companies: Anti Counterfeiting Technology Companies
The global market for anti-counterfeiting technology is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing instances of counterfeiting across various industries and a rising consumer awareness of the risks associated with purchasing fake products. This growth is fueled by advancements in technology, stricter government regulations, and the increasing sophistication of counterfeiters themselves. Understanding the market landscape, including key players and technological trends, is crucial for both businesses seeking to protect their brands and investors looking for opportunities in this dynamic sector.
The anti-counterfeiting technology market is highly competitive, with a diverse range of companies offering various solutions. While precise market share data for individual companies is often proprietary and unavailable publicly, several key players dominate specific segments. The market is further segmented by the technology employed, creating a complex and evolving ecosystem.
Market Segmentation by Technology Type
The anti-counterfeiting technology market can be broadly categorized by the core technology utilized. Several technologies are prevalent, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages depending on the application and industry. These technologies often work in conjunction, offering multi-layered protection.
Major Players and Market Share (Illustrative Data)
Precise market share figures for individual companies are difficult to obtain due to the competitive nature of the industry and the lack of publicly available comprehensive data. The following table provides an illustrative representation based on available information and market analysis reports, recognizing that actual figures may vary. This data should be considered an approximation, not a definitive statement of market share.
| Company Name | Approximate Market Share (%) | Technology Used | Geographic Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Authentix | (Illustrative: Assume 5-10%) | RFID, Track and Trace | Global, with strong presence in North America and Europe |
| Applied DNA Sciences | (Illustrative: Assume 3-7%) | DNA Tagging | Global, with significant focus on pharmaceuticals and textiles |
| OpSec Security | (Illustrative: Assume 8-15%) | Holography, Microprinting, other overt and covert security features | Global, strong presence in various industries |
| Checkpoint Systems | (Illustrative: Assume 10-18%) | RFID, EAS (Electronic Article Surveillance) | Global, strong in retail and apparel |
| Several smaller players and niche technology providers | (Illustrative: Assume remaining share) | Blockchain, AI-powered image recognition, digital watermarking, etc. | Varied, often regionally focused |
Note: The market share percentages provided are illustrative and based on estimations from industry reports and analyses. Actual market share may differ. The companies listed are examples and do not represent an exhaustive list of all players in the market.
Technological Advancements in Anti-Counterfeiting
The fight against counterfeiting is a constant arms race, with innovators developing ever more sophisticated techniques to protect brands and consumers. Recent advancements leverage cutting-edge technologies across various sectors, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in securing products and verifying authenticity. This section will explore some of the most significant technological advancements, their advantages and disadvantages, and compare several key approaches.
Holographic Security Technologies
Holographic images offer a visually striking and difficult-to-replicate method of anti-counterfeiting. These three-dimensional images are created using lasers to interfere light patterns, resulting in a complex, iridescent effect that shifts and changes with viewing angle. Modern advancements include incorporating micro-text, dynamic features, and even embedded security codes within the hologram itself, making them significantly harder to forge.
- Key Features: Visually complex, difficult to replicate, can incorporate additional security features.
- Applications: Packaging, labels, high-value products (e.g., pharmaceuticals, luxury goods).
- Advantages: High visual deterrent, readily apparent to consumers.
- Disadvantages: Can be relatively expensive to implement, requires specialized equipment for production.
Track and Trace Systems
Track and trace systems utilize unique identifiers (e.g., barcodes, RFID tags, serial numbers) to monitor the movement of products throughout the supply chain. This provides a detailed audit trail, enabling businesses to identify and isolate counterfeit goods. Advanced systems integrate with blockchain technology to enhance security and transparency, creating an immutable record of each product’s journey.
- Key Features: Detailed product tracking, enhanced supply chain visibility, often integrated with blockchain technology.
- Applications: Pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, high-value electronics.
- Advantages: Provides comprehensive tracking data, helps identify counterfeiters, improves supply chain efficiency.
- Disadvantages: Can be expensive to implement, requires infrastructure investment across the supply chain.
Digital Watermarking
Digital watermarking embeds imperceptible codes into digital content (e.g., images, audio, video) that can be used to verify authenticity. These watermarks are designed to be robust against various attacks, such as compression or cropping. Advancements in this field include developing watermarks that are resilient to sophisticated manipulation techniques and integrating them with AI-powered detection systems. For example, a company might embed a unique watermark into the digital image of a product’s packaging, which can then be verified using specialized software.
- Key Features: Imperceptible codes embedded within digital content, robust against manipulation, often integrated with AI-powered detection.
- Applications: Digital media, software, online documents.
- Advantages: Cost-effective for digital products, relatively easy to implement.
- Disadvantages: Can be vulnerable to sophisticated attacks, requires specialized software for detection.
Comparison of Technologies
While each technology offers unique advantages, their suitability depends heavily on the specific application and budget. Holograms provide a strong visual deterrent and are effective for physical products, but are more expensive to implement than digital watermarks. Track and trace systems excel at providing comprehensive supply chain visibility, but require significant infrastructure investment. Digital watermarks are cost-effective for digital content but may be more vulnerable to sophisticated attacks compared to holograms or robust track and trace systems. The optimal solution often involves a multi-layered approach, combining several technologies to maximize security. For instance, a pharmaceutical company might use holograms on packaging, RFID tags for tracking, and digital watermarks on accompanying documentation to create a comprehensive anti-counterfeiting strategy.
Industry Applications of Anti-Counterfeiting Technologies
The proliferation of counterfeit goods poses a significant threat across numerous industries, impacting brand reputation, consumer safety, and economic stability. The effectiveness of anti-counterfeiting technologies varies depending on the specific industry and the nature of the product, but their application is crucial in mitigating these risks. This section will explore the application of these technologies across several key sectors.
Industries Most Vulnerable to Counterfeiting
Several industries are particularly susceptible to counterfeiting due to factors such as high profit margins, complex supply chains, and difficulty in verifying authenticity. The pharmaceutical industry, luxury goods sector, and the food and beverage industry consistently face significant challenges from counterfeiters. High-value products, those requiring specialized knowledge to authenticate, and those easily replicated are prime targets. The ease of online sales further exacerbates the problem, making it harder to control the distribution and sale of counterfeit goods.
Anti-Counterfeiting Technologies in the Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry faces exceptionally high stakes when it comes to counterfeiting. Counterfeit drugs can be ineffective, contain harmful ingredients, or have incorrect dosages, posing serious risks to public health. To combat this, various anti-counterfeiting technologies are employed. These include serialization, where each drug package is assigned a unique identifier, track and trace systems that monitor the movement of pharmaceuticals throughout the supply chain, and the use of overt and covert security features such as holograms, microprinting, and special inks on packaging. Furthermore, blockchain technology is increasingly being used to create secure, tamper-proof records of drug movement and authenticity. This technology enhances transparency and accountability across the supply chain, making it more difficult for counterfeiters to infiltrate.
Anti-Counterfeiting Technologies in the Luxury Goods Sector, Anti counterfeiting technology companies
The luxury goods industry is another sector significantly impacted by counterfeiting. The high value and aspirational nature of these products make them attractive targets for counterfeiters. Brands employ a range of strategies to combat this. These include using sophisticated RFID tags embedded in products to verify authenticity, incorporating unique serial numbers and holograms into packaging and products themselves, and leveraging blockchain technology to track the provenance of high-value items. Moreover, authentication apps are becoming increasingly common, allowing consumers to verify the authenticity of luxury goods by scanning a unique code or using image recognition technology. This empowers consumers to make informed purchases and discourages the purchase of counterfeit goods.
Hypothetical Implementation Plan: Anti-Counterfeiting in the Food and Beverage Industry
A comprehensive anti-counterfeiting strategy for the food and beverage industry would involve a multi-faceted approach. Firstly, a robust track and trace system utilizing RFID tags or barcodes at each stage of the supply chain, from production to retail, would allow for better monitoring and identification of potentially counterfeit products. Secondly, the implementation of tamper-evident packaging, incorporating features like seals and unique markings, would alert consumers to any tampering or counterfeiting attempts. Thirdly, the use of blockchain technology to record and verify the origin and journey of food products could enhance transparency and accountability. This would involve collaborating with suppliers and retailers to ensure data integrity and accessibility. Finally, a public awareness campaign would educate consumers on how to identify counterfeit products and report suspicious activity. This could include providing information on common counterfeit indicators and promoting the use of authentication apps or websites. A successful implementation would necessitate collaboration between industry stakeholders, regulatory bodies, and consumers.
Challenges and Opportunities in Anti-Counterfeiting

The anti-counterfeiting technology market, while experiencing significant growth, faces considerable hurdles in achieving widespread adoption and realizing its full potential. These challenges stem from a complex interplay of technological limitations, economic factors, and regulatory issues, all impacting the effectiveness and accessibility of these crucial solutions. However, alongside these challenges lie compelling opportunities driven by technological advancements and expanding market needs.
Technological Limitations and High Implementation Costs
A primary obstacle to widespread adoption is the inherent complexity and cost associated with implementing advanced anti-counterfeiting technologies. Many sophisticated solutions, such as blockchain-based tracking systems or sophisticated micro-printing techniques, require substantial upfront investment in specialized equipment, software, and skilled personnel. This can be particularly prohibitive for smaller businesses or those operating in developing economies, where the prevalence of counterfeiting is often highest. Furthermore, the constant evolution of counterfeiting methods necessitates continuous updates and upgrades to anti-counterfeiting technologies, adding to the ongoing expense. This creates a barrier to entry for many companies, limiting the overall impact of these technologies. For example, a small artisan producer of handcrafted goods might find the cost of implementing a sophisticated track-and-trace system disproportionate to their budget, leaving them vulnerable to counterfeiting.
Lack of Standardization and Interoperability
The absence of widely accepted industry standards for anti-counterfeiting technologies presents a significant challenge. Different technologies employ varying methods of authentication and data management, making it difficult to integrate them seamlessly into existing supply chains. This lack of interoperability limits the effectiveness of anti-counterfeiting efforts, as a fragmented approach makes it easier for counterfeiters to circumvent individual systems. For instance, a company using a specific RFID tagging system might find it challenging to share data effectively with a partner using a different, incompatible technology, hindering collaborative efforts to combat counterfeiting.
Consumer Awareness and Education
Effective anti-counterfeiting relies not only on robust technologies but also on informed consumers who can identify and avoid counterfeit products. A lack of awareness among consumers regarding the existence and use of anti-counterfeiting measures significantly reduces the impact of these technologies. Many consumers are unaware of how to verify the authenticity of products, making them vulnerable to deception. Educational campaigns and clear, accessible labeling are crucial to bridge this gap and empower consumers to make informed purchasing decisions. For example, a clear visual indicator on packaging, coupled with a readily accessible verification method (like a QR code linked to a product authenticity database), can significantly improve consumer confidence and participation in anti-counterfeiting efforts.
Emerging Opportunities: AI-Powered Authentication and Expanding Market Sectors
Despite the challenges, the anti-counterfeiting market is experiencing substantial growth driven by technological advancements and expanding market sectors. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is revolutionizing authentication processes, enabling faster, more accurate, and more efficient detection of counterfeit goods. AI-powered systems can analyze vast datasets to identify subtle patterns and anomalies indicative of counterfeiting, improving detection rates and reducing false positives. Moreover, the application of anti-counterfeiting technologies is expanding beyond traditional sectors like pharmaceuticals and luxury goods, into new areas such as food and beverage, cosmetics, and even digital content. The increasing demand for product authenticity across various industries presents significant opportunities for anti-counterfeiting technology providers. For example, the growing concern about food safety and the prevalence of counterfeit food products are driving the adoption of blockchain-based traceability systems in the food and beverage industry.
Regulatory Landscape and Legal Frameworks
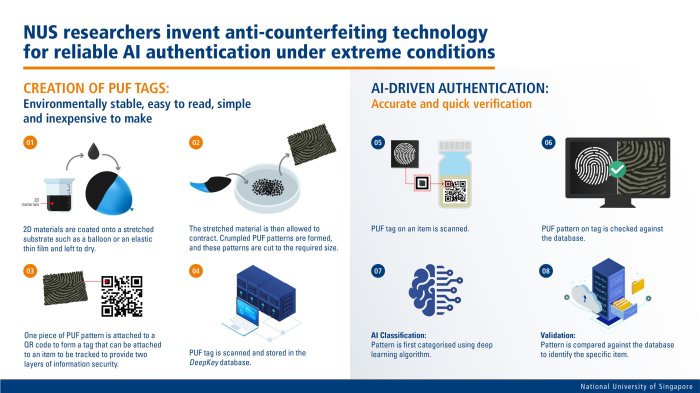
The global fight against counterfeiting relies heavily on a complex web of international treaties, national laws, and enforcement mechanisms. Understanding these legal frameworks is crucial for anti-counterfeiting technology companies, as their technologies often play a vital role in supporting legal actions and preventative measures. The effectiveness of these frameworks varies significantly across jurisdictions, impacting the success of anti-counterfeiting strategies.
The role of intellectual property rights (IPR) in combating counterfeiting is paramount. IPR, encompassing patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets, provides legal protection for the creators and owners of original works and inventions. Infringement of these rights forms the basis of many legal actions against counterfeiters. Strong IPR protection deters counterfeiting by making it a legally risky and potentially costly endeavor. However, the enforcement of these rights varies greatly across countries, with some having more robust legal systems and enforcement agencies than others.
Intellectual Property Rights and Anti-Counterfeiting
Intellectual property rights (IPR) are the cornerstone of anti-counterfeiting efforts. Patents protect inventions, trademarks safeguard brand identities, copyrights protect creative works, and trade secrets safeguard confidential information. When counterfeiters reproduce or imitate products or designs protected by IPR, they infringe these rights, making them liable for legal action. The strength of IPR protection and the effectiveness of its enforcement vary considerably across countries, significantly influencing the success of anti-counterfeiting measures. For example, a strong patent system discourages the counterfeiting of technologically advanced products, while robust trademark protection prevents the unauthorized use of brand names and logos.
Comparative Analysis of Legal Frameworks
The following table compares the legal frameworks and enforcement mechanisms related to counterfeiting in three different countries: the United States, the European Union, and China. These represent diverse legal systems and approaches to combating counterfeiting.
| Country/Region | Key Legislation & Regulations | Enforcement Agencies | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Lanham Act (trademarks), Copyright Act, Patent Act, various customs laws. Also, the Stop Counterfeiting in Manufactured Goods Act (SCMGA). | U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP), Federal Trade Commission (FTC), Department of Justice (DOJ). | Strong emphasis on civil litigation, significant penalties for infringement, robust customs enforcement. SCMGA provides criminal penalties for large-scale counterfeiting. |
| European Union | EU Trademark Regulation, EU Copyright Directive, various national laws harmonized under EU frameworks. | National customs authorities, national police forces, specialized agencies (e.g., OLAF). | Harmonized legal framework across member states, focus on cross-border enforcement cooperation, increasing emphasis on criminal sanctions. |
| China | Trademark Law, Patent Law, Copyright Law, Anti-Unfair Competition Law. | State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR), Public Security Bureau, customs authorities. | Rapidly evolving legal framework, increasing efforts to combat counterfeiting, challenges remain in enforcement and judicial efficiency. Focus on both criminal and civil penalties. |
Consumer Awareness and Education
Consumer education plays a crucial role in combating the counterfeit market. By empowering consumers to make informed purchasing decisions, we significantly reduce the demand that fuels the counterfeiting industry. This, in turn, lessens the profitability of counterfeiters and encourages a shift towards legitimate products.
Educating consumers about identifying counterfeit goods involves a multi-pronged approach encompassing various strategies and mediums. Successful campaigns leverage a combination of accessible information, engaging content, and readily available resources to help consumers differentiate authentic products from their imitations.
Strategies for Educating Consumers
Effective consumer education requires a clear and concise approach. Providing consumers with practical tools and information makes it easier for them to distinguish between genuine and counterfeit products. This involves highlighting key differences in packaging, labeling, and product features, as well as explaining the risks associated with purchasing counterfeit goods. The information should be presented in easily digestible formats across multiple platforms.
Examples of Successful Consumer Awareness Campaigns
Several organizations have launched successful campaigns to raise consumer awareness. For instance, the International Anti-Counterfeiting Coalition (IACC) regularly publishes educational materials and resources for consumers. Many brand-specific campaigns focus on educating consumers about specific product authentication methods. These campaigns often utilize social media, websites, and in-store displays to reach their target audiences. The success of these campaigns is often measured by changes in consumer purchasing behavior and reported instances of counterfeit purchases.
Sample Infographic: Identifying Counterfeit Products
This infographic uses descriptive text to illustrate how to identify counterfeit products. Imagine a visual representation divided into sections:
Section 1: Packaging: The genuine product’s packaging will be of high quality, with crisp printing, accurate spelling and grammar, and consistent branding. Counterfeit packaging often displays blurry images, misspellings, and inconsistencies in font styles or logos. The packaging materials themselves might feel cheap or flimsy compared to the authentic product.
Section 2: Labeling: Legitimate labels will have clear and accurate information, including the manufacturer’s details, country of origin, and any relevant certifications or trademarks. Counterfeit labels often lack these details or contain inconsistencies, blurry images, or incorrect information. The barcodes may not scan correctly, or the text may be poorly translated.
Section 3: Product Features: Genuine products typically have precise details and consistent construction. Counterfeit products often exhibit inconsistencies in stitching, material quality, or overall finish. Small details such as logos, engravings, or serial numbers might be poorly replicated or missing entirely. Functionality may also be compromised in counterfeit goods. For example, a counterfeit electronic device might malfunction frequently or have significantly shorter battery life.
Section 4: Price: If a deal seems too good to be true, it probably is. Substantially lower prices compared to the genuine product’s market value are a significant indicator of counterfeiting. Be wary of exceptionally low prices, especially when purchased from unfamiliar or untrusted sellers.
Section 5: Seller Reputation: Purchase products from reputable retailers and authorized sellers. Avoid purchasing from unknown or unverified online sellers, especially those with poor reviews or lacking contact information. Verify seller legitimacy before making a purchase.
Future Trends in Anti-Counterfeiting Technology
The fight against counterfeiting is constantly evolving, driven by the ingenuity of counterfeiters and the innovative responses of anti-counterfeiting technology developers. Emerging technologies are poised to revolutionize how we protect brands and consumers, shifting the landscape from reactive measures to proactive, even predictive, strategies. This section explores several key future trends and their potential impact.
The future of anti-counterfeiting hinges on the convergence of several technological advancements, creating a more sophisticated and interconnected system of protection. This interconnectedness will allow for real-time tracking, verification, and response to counterfeiting activities, significantly reducing the impact of fraudulent products on legitimate businesses and consumers.
Anti-counterfeiting technology companies are constantly innovating to stay ahead of sophisticated counterfeiters. A key aspect of their strategies often involves leveraging single source technologies to ensure the authenticity and traceability of products. This reliance on single-source solutions helps these companies maintain control over their supply chains and protect their brand integrity from fraudulent replication.
Blockchain Technology’s Expanding Role
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent method for tracking products throughout their supply chain. Each product can be assigned a unique digital identity, verifiable on the blockchain, making it nearly impossible to replicate or alter. This provides a permanent record of the product’s journey, from manufacturing to the consumer, allowing for immediate authentication and detection of counterfeit goods. For example, luxury brands could use blockchain to record the entire production history of a handbag, from the source of the leather to the final stitching, creating an immutable record of authenticity. This level of transparency not only combats counterfeiting but also builds consumer trust and brand loyalty.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in Counterfeit Detection
AI and ML algorithms are rapidly improving their ability to identify counterfeit products based on subtle visual or physical differences often missed by the human eye. These algorithms can analyze images, videos, and even sensor data to detect anomalies indicative of counterfeiting. Furthermore, AI can be used to predict potential counterfeiting hotspots or trends, allowing for proactive interventions. Imagine a system that analyzes online marketplaces in real-time, flagging suspicious listings based on image analysis and pricing patterns. This predictive capability is crucial in staying ahead of counterfeiters and reducing the spread of fraudulent products.
Advanced Material Science and Nanotechnology
The development of new materials and nanotechnologies is providing innovative ways to embed unique identifiers into products. These identifiers can be nearly impossible to replicate without sophisticated equipment, providing an additional layer of security. For instance, specialized inks that change color under specific light conditions or nanostructures that emit unique spectral signatures are being developed and implemented. These technologies make it far more difficult to create convincing counterfeits.
A Future Scenario: The Fashion Industry
Consider the fashion industry in five years. High-end fashion houses utilize blockchain to track every stage of garment production, from the raw materials to the final product. Consumers can scan a QR code on a garment’s label to access its complete provenance, including images and videos from each stage of the production process. AI-powered systems constantly monitor online marketplaces and social media for counterfeit products, automatically flagging suspicious listings and alerting authorities. Advanced materials, such as self-authenticating fabrics embedded with microscopic identifiers, are becoming increasingly common. This holistic approach creates a highly secure ecosystem that significantly reduces the impact of counterfeiting on the industry and protects consumers from purchasing fake products.
Case Studies of Successful Anti-Counterfeiting Initiatives
The fight against counterfeiting requires innovative strategies and robust technologies. Examining successful anti-counterfeiting initiatives reveals best practices and highlights the crucial factors contributing to their effectiveness. The following case studies illustrate diverse approaches and their impact across various industries.
Successful Anti-Counterfeiting Initiatives: Case Study Examples
Several companies have successfully implemented anti-counterfeiting measures, leading to significant reductions in counterfeit products and improved brand protection. These successes demonstrate the value of a multi-faceted approach combining technology, legal action, and consumer education.
| Company | Industry | Technology Used | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| LVMH (Louis Vuitton Moët Hennessy) | Luxury Goods | RFID tags, blockchain technology, holograms, unique serial numbers, sophisticated packaging, legal action against counterfeiters | Significant reduction in counterfeit products, improved brand reputation and consumer trust. The combination of technologies makes it significantly more difficult to replicate their products effectively. Legal actions have deterred many counterfeiters. |
| Nike | Apparel and Footwear | Unique product codes, RFID tags, advanced materials science (making counterfeiting more difficult), partnerships with retailers to verify authenticity, robust legal enforcement. | Improved brand protection, reduced counterfeit sales, and enhanced consumer confidence in the authenticity of their products. Nike’s multi-pronged approach, focusing on both technology and legal channels, has been particularly effective. |
| Pharmaceutical Companies (e.g., GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer) | Pharmaceuticals | Track and trace systems using serialization and aggregation, tamper-evident packaging, unique identification numbers, blockchain technology for supply chain transparency. | Reduced the circulation of counterfeit drugs, improved patient safety, and enhanced supply chain security. The use of serialization and aggregation technologies allows for better tracking of products throughout the supply chain, making it easier to identify and remove counterfeit products. |
Factors Contributing to Success
The success of these initiatives stems from a combination of factors. A crucial element is the integration of multiple technologies, creating a layered approach that makes counterfeiting significantly more complex and costly. Strong legal action against counterfeiters is also vital, deterring future attempts. Finally, consumer education plays a crucial role in raising awareness and empowering consumers to identify and avoid counterfeit products.
Best Practices for Implementing Anti-Counterfeiting Programs
Effective anti-counterfeiting programs require a holistic strategy encompassing technological solutions, legal measures, and consumer engagement. Best practices include:
- Implementing a multi-layered security approach using various technologies.
- Establishing strong partnerships with retailers and distributors to ensure product authenticity throughout the supply chain.
- Actively pursuing legal action against counterfeiters.
- Educating consumers on how to identify counterfeit products.
- Regularly reviewing and updating anti-counterfeiting strategies to adapt to evolving counterfeiting techniques.
Economic Impact of Counterfeiting and Anti-Counterfeiting Measures
Counterfeiting inflicts significant economic damage on businesses, consumers, and governments worldwide, impacting various sectors and leading to substantial financial losses. Conversely, implementing robust anti-counterfeiting measures can mitigate these losses and foster economic growth by protecting legitimate businesses and enhancing consumer trust. This section details the economic consequences of counterfeiting and the economic benefits derived from anti-counterfeiting strategies.
Economic Impact of Counterfeiting on Businesses and Consumers
Counterfeiting undermines legitimate businesses by eroding market share, reducing revenue, and damaging brand reputation. Businesses face increased costs associated with legal battles, investigations, and the development and implementation of anti-counterfeiting measures. Consumers, on the other hand, risk purchasing substandard or dangerous products, leading to financial losses, safety hazards, and a diminished confidence in the marketplace. The impact extends beyond direct financial losses; counterfeiting can stifle innovation, hinder economic growth, and negatively affect employment levels within legitimate industries. For example, the International Anti-Counterfeiting Coalition (IACC) estimates that counterfeiting costs businesses billions of dollars annually in lost revenue and increased security expenses.
Economic Benefits of Implementing Anti-Counterfeiting Measures
Investing in anti-counterfeiting measures provides substantial economic benefits. These measures protect intellectual property rights, preserving brand value and market share for legitimate businesses. Reduced counterfeiting leads to increased revenue, improved profitability, and enhanced consumer confidence. Furthermore, strong anti-counterfeiting strategies foster innovation by encouraging companies to invest in research and development without the fear of their intellectual property being easily copied. The creation of secure products also reduces safety risks to consumers, avoiding potential health issues or financial losses due to faulty or dangerous counterfeit goods. A study by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) highlights the positive correlation between robust intellectual property protection and economic growth.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Implementing a Specific Anti-Counterfeiting Technology
Let’s consider the implementation of track-and-trace technology using blockchain for a pharmaceutical company. The initial investment would include software development, hardware integration, and employee training. Ongoing costs would encompass maintenance, updates, and data storage. However, the benefits would include reduced counterfeiting, improved supply chain visibility, enhanced brand protection, and increased consumer trust. This would lead to higher sales, reduced legal costs, and a stronger brand reputation. A quantitative cost-benefit analysis would require specific data on the company’s current counterfeiting losses, the cost of implementing the blockchain technology, and the projected reduction in counterfeiting and increase in sales following implementation. While a precise calculation requires company-specific data, the potential return on investment (ROI) can be significant, particularly for industries with high levels of counterfeiting, like pharmaceuticals.
Economic Impact of Counterfeiting on the Apparel Industry
Imagine a visual representation: a bar graph showing the revenue of a major apparel brand. One bar represents legitimate sales, showing a substantial figure. Next to it, a significantly smaller bar represents the lost revenue due to counterfeiting. A third bar, even smaller, shows the costs associated with anti-counterfeiting measures. The visual clearly demonstrates that while anti-counterfeiting measures incur costs, the losses from counterfeiting are far greater, highlighting the economic imperative of implementing such measures. The apparel industry is particularly vulnerable to counterfeiting, with significant losses reported annually due to the ease of replicating designs and the high demand for branded apparel. This loss impacts not only the brand’s bottom line but also the jobs supported by the legitimate industry. Furthermore, the sale of counterfeit apparel often involves unsafe working conditions and unethical labor practices in their production, creating further negative economic and social consequences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the anti-counterfeiting technology sector is dynamic and vital, constantly evolving to combat sophisticated counterfeiting techniques. While challenges remain, the ongoing development of innovative technologies, coupled with increased consumer awareness and strengthened legal frameworks, offers a promising outlook for effectively mitigating the global threat of counterfeiting. The future likely holds even more advanced solutions, integrating artificial intelligence and blockchain technologies for unprecedented levels of product authentication and traceability.
The rise of sophisticated anti-counterfeiting technology companies is crucial in today’s market. These companies often leverage complex data analysis and security measures to combat fraud. However, financial technology companies like sofi technologies also play a vital role by implementing robust security protocols to protect customer data and transactions, indirectly aiding in the fight against counterfeiting.
Ultimately, a multi-pronged approach involving both specialized anti-counterfeiting firms and financial institutions is necessary for effective protection.





