Amkor Technology stands as a global leader in semiconductor packaging and test services, a critical component of the modern electronics industry. This exploration delves into Amkor’s multifaceted operations, examining its business model, market position, financial performance, technological innovations, and future outlook. We will also analyze its supply chain, customer relationships, and commitment to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles. The company’s strategic priorities and the challenges it faces will be carefully considered.
Understanding Amkor Technology requires a nuanced perspective, encompassing its intricate global network, technological expertise, and strategic partnerships. This analysis aims to provide a clear and comprehensive understanding of this significant player in the semiconductor landscape.
Amkor Technology’s Business Model
Amkor Technology operates as a leading provider of outsourced semiconductor packaging and test services. Their business model centers around providing a comprehensive suite of services to semiconductor companies, allowing them to focus on design and development while Amkor handles the complex and capital-intensive processes of packaging and testing their chips. This ultimately reduces costs and accelerates time-to-market for their clients.
Amkor Technology’s core business operations revolve around transforming bare semiconductor dies into finished packaged products ready for integration into various electronic devices. Revenue streams are primarily generated through fees charged for these packaging and testing services, which vary depending on the complexity and volume of the orders. The company’s success hinges on its ability to offer efficient, high-quality services at competitive prices, while maintaining strong relationships with a diverse customer base.
Amkor Technology’s Service Offerings
Amkor offers a wide range of packaging and test services catering to diverse customer needs and product types. These services include, but are not limited to, wafer bumping, wafer probing, die preparation, various packaging technologies (such as wire bonding, flip-chip, system-in-package, and others), final test, and advanced packaging solutions. Their offerings span across multiple semiconductor technologies, encompassing everything from memory chips to microprocessors and other specialized integrated circuits. The breadth and depth of their service portfolio allow them to serve a broad spectrum of the semiconductor industry.
Comparison with Competitors
Amkor Technology competes with other large players in the outsourced semiconductor packaging and testing market, including companies like ASE Technology Holding and SPIL (Siliconware Precision Industries). While all three companies offer similar core services, subtle differences exist in their strategic focus and technological capabilities. For example, Amkor might emphasize its expertise in a specific packaging technology, such as advanced 3D packaging, while a competitor might focus more on high-volume manufacturing of simpler packages. Competitive advantages are often driven by factors like technological leadership, manufacturing efficiency, geographic reach, and customer relationships. Pricing strategies and contract terms also play a crucial role in securing and retaining customers within this highly competitive landscape. Direct comparison requires detailed financial data and market analysis specific to each company’s performance in various market segments.
Amkor Technology’s Market Position
Amkor Technology holds a significant position within the global semiconductor packaging and test industry, operating across diverse market segments and geographical regions. Understanding their market share, competitive advantages, and disadvantages is crucial to assessing their overall strength and future prospects. This section will detail Amkor’s market standing, providing insights into their key areas of operation and competitive landscape.
Amkor Technology’s key market segments and geographic regions are diverse and reflect the broad nature of the semiconductor industry.
Market Segments and Geographic Regions
Amkor Technology serves a wide range of end markets, including communications, computing, consumer, industrial, and automotive. Within these sectors, they cater to diverse customer needs, ranging from large multinational corporations to smaller, specialized companies. Their geographic reach is extensive, with significant operations in Asia (particularly in China, Korea, Malaysia, and the Philippines), the Americas (including the United States and Mexico), and Europe. This global presence allows Amkor to serve customers worldwide and respond effectively to evolving market demands. This geographically diverse manufacturing footprint also helps mitigate risks associated with regional economic fluctuations or geopolitical events.
Amkor Technology’s Market Share
Precise market share figures for Amkor Technology are not consistently published due to the competitive nature of the industry and the varying methodologies used for market analysis. However, Amkor is consistently ranked among the top three or four companies globally in the outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) market. This positioning indicates a substantial market share, though the exact percentage fluctuates depending on the specific year and the market segment considered. Industry reports from reputable firms such as Gartner and IC Insights can provide more granular data on market share dynamics, though these reports often require subscription access.
Competitive Advantages and Disadvantages
Amkor Technology’s competitive advantages stem from several key factors. Their global manufacturing footprint provides logistical advantages and allows them to serve customers with diverse needs. Their extensive technological expertise, encompassing a wide range of packaging technologies, allows them to offer flexible solutions to customers. Furthermore, Amkor’s long-standing relationships with key semiconductor companies provide a significant competitive edge. Their scale and experience also contribute to cost efficiencies.
However, Amkor also faces competitive disadvantages. The OSAT market is highly competitive, with several large players vying for market share. Price pressure from customers is a constant challenge. Technological innovation is rapid, requiring continuous investment in research and development to maintain a competitive edge. Geopolitical factors and regional economic fluctuations also pose risks to their operations. Finally, dependence on a few large customers can create vulnerability to changes in those customers’ strategies or demand.
Amkor Technology’s Financial Performance
Amkor Technology’s financial performance reflects the cyclical nature of the semiconductor industry and its position within the outsourced assembly and test (OSAT) market. Analyzing key financial metrics provides insights into the company’s profitability, operational efficiency, and overall financial health. Understanding these trends is crucial for investors and stakeholders alike.
Amkor Technology’s recent financial results have shown a mixed bag, influenced by fluctuating demand for semiconductors and global economic conditions. While revenue has generally trended upwards in recent years, profit margins have experienced some volatility, largely due to variations in production costs and pricing pressures within the competitive OSAT landscape. The company’s financial performance is closely tied to the overall health of the semiconductor industry and its ability to secure contracts with major semiconductor manufacturers.
Key Financial Ratios and Metrics
Several key financial ratios and metrics are instrumental in evaluating Amkor Technology’s financial performance. These include gross margin, operating margin, net income margin, return on assets (ROA), and return on equity (ROE). Gross margin reveals the profitability of Amkor’s core operations, while operating and net income margins illustrate efficiency in managing expenses and overall profitability. ROA and ROE reflect the company’s effectiveness in utilizing assets and equity to generate profits. Analyzing trends in these ratios over time offers valuable insights into the company’s financial health and performance. For example, a declining gross margin might indicate increased production costs or pricing pressures, while a rising ROA suggests improved asset management.
Amkor Technology’s Revenue, Profit, and Expenses (Past Five Years)
The following table summarizes Amkor Technology’s revenue, profit, and expenses over the past five years. Note that these figures are illustrative and should be verified using Amkor Technology’s official financial statements. Actual figures may vary slightly depending on the reporting period and accounting practices.
| Year | Revenue (USD Millions) | Profit (USD Millions) | Expenses (USD Millions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 5500 | 500 | 5000 |
| 2021 | 5000 | 400 | 4600 |
| 2020 | 4500 | 300 | 4200 |
| 2019 | 4000 | 250 | 3750 |
| 2018 | 3800 | 200 | 3600 |
Amkor Technology’s Technology and Innovation
Amkor Technology’s success is deeply rooted in its advanced technological capabilities and continuous investment in research and development. The company leverages a diverse portfolio of technologies to provide comprehensive solutions for its customers’ semiconductor packaging needs, consistently pushing the boundaries of miniaturization, performance, and cost-effectiveness. This commitment to innovation ensures Amkor remains a leading player in the global outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) market.
Amkor Technology possesses significant expertise across a wide range of semiconductor packaging technologies. This includes advanced packaging techniques like system-in-package (SiP), 2.5D/3D packaging, flip-chip, wire bonding, and various other interconnect technologies. Their capabilities extend to diverse materials and processes, enabling them to cater to a broad spectrum of customer requirements, from high-volume consumer electronics to high-reliability applications in the automotive and aerospace sectors.
Amkor Technology’s Research and Development Investments
Amkor’s commitment to innovation is reflected in its substantial investment in research and development. This investment fuels the development of new packaging technologies, process improvements, and advanced materials. The company collaborates extensively with leading equipment manufacturers and research institutions to stay at the forefront of technological advancements. A significant portion of R&D expenditure is directed towards improving yield, reducing costs, and enhancing the performance and reliability of its packaging solutions. This proactive approach allows Amkor to meet the ever-evolving demands of the semiconductor industry and maintain a competitive edge. Specific examples of R&D successes could include the development of new packaging materials with improved thermal conductivity or the refinement of processes leading to higher yields and lower production costs. These achievements are often showcased in technical publications and industry presentations.
Comparison of Amkor Technology’s Key Technologies with Competitors
The following table compares Amkor Technology’s key technologies with those of two unnamed competitors (Competitor A and Competitor B) to illustrate Amkor’s competitive standing. Note that specific details regarding competitor capabilities are often commercially sensitive and publicly available information may be limited. This table presents a generalized comparison based on publicly available information and industry knowledge.
| Technology | Amkor | Competitor A | Competitor B |
|---|---|---|---|
| System-in-Package (SiP) | Advanced SiP capabilities, including heterogeneous integration | Offers SiP solutions, but potentially less advanced capabilities in heterogeneous integration | Strong SiP capabilities, focusing on specific market segments |
| 2.5D/3D Packaging | Extensive experience in both 2.5D and 3D packaging technologies | Limited experience in 3D packaging; primarily focuses on 2.5D | Significant expertise in 3D packaging, but potentially less experience in 2.5D |
| Flip-Chip | High-volume flip-chip production capabilities | Offers flip-chip services, but may lack Amkor’s scale | Competitive in flip-chip technology, focusing on high-end applications |
| Wire Bonding | Advanced wire bonding techniques for high-density applications | Standard wire bonding capabilities | Advanced wire bonding capabilities, specializing in specific materials |
Amkor Technology’s Supply Chain and Manufacturing
Amkor Technology’s success hinges significantly on its robust global supply chain and efficient manufacturing capabilities. The company’s extensive network allows it to serve a diverse clientele across various industries, while its advanced manufacturing processes ensure high-quality products delivered on time. This section details Amkor’s manufacturing footprint, key relationships, and the inherent challenges within its operational framework.
Amkor Technology operates a globally distributed manufacturing network, leveraging multiple facilities strategically located across Asia, North America, and Europe. This geographically diverse approach enables the company to serve customers worldwide, reducing lead times and mitigating risks associated with regional disruptions. The facilities are equipped with state-of-the-art semiconductor packaging and testing equipment, reflecting a commitment to technological advancement and operational excellence. This distributed network allows for efficient management of production and supply, optimizing resource allocation and responding quickly to fluctuations in demand.
Amkor Technology’s Global Manufacturing Footprint
Amkor’s manufacturing facilities are strategically positioned to serve major semiconductor markets. Key locations include facilities in China, Korea, Malaysia, the Philippines, and the United States. Each facility specializes in different aspects of semiconductor packaging and testing, allowing for efficient workflow and specialized expertise. This distributed approach offers redundancy and resilience against potential disruptions in any single location. For instance, if one facility experiences unforeseen challenges, Amkor can seamlessly redirect production to another facility to minimize disruptions to customer orders.
Amkor Technology’s Key Suppliers and Customers
Identifying specific suppliers and customers for Amkor Technology requires accessing confidential business information, which is generally not publicly disclosed due to competitive sensitivities and contractual obligations. However, it’s understood that Amkor’s supplier base includes a wide range of materials providers, equipment manufacturers, and specialized service providers within the semiconductor industry. Similarly, Amkor’s customer base is comprised of leading companies in various sectors, including consumer electronics, automotive, communications, and industrial applications. These customers rely on Amkor’s packaging and testing services to ensure the quality and reliability of their integrated circuits.
Challenges and Risks in Amkor Technology’s Supply Chain
Amkor Technology’s supply chain, like many in the semiconductor industry, faces several significant challenges. Geopolitical instability, natural disasters, and pandemics can disrupt supply lines and production schedules. Fluctuations in raw material prices and component availability pose ongoing risks. Furthermore, managing the complexity of a global network, including logistics, customs, and regulatory compliance, requires significant operational expertise and resources. Maintaining high levels of quality control across multiple facilities is also crucial to upholding Amkor’s reputation and meeting customer expectations. The semiconductor industry’s reliance on highly specialized equipment and skilled labor also creates vulnerabilities. A shortage of skilled workers or equipment failures can significantly impact production capacity and delivery timelines. Mitigation strategies include diversification of suppliers, robust risk management protocols, and continuous investment in technological upgrades and employee training.
Amkor Technology’s Customer Base
Amkor Technology boasts a diverse and extensive customer base, primarily composed of leading companies in the semiconductor industry. These clients span various sectors, relying on Amkor’s advanced packaging and testing services to bring their innovative products to market. Understanding Amkor’s key customer relationships is crucial to assessing the company’s overall health and future prospects.
Amkor’s client relationships are built on a foundation of long-term partnerships, collaboration, and mutual success. The company prioritizes close engagement with its customers, working collaboratively to develop customized solutions that meet specific product requirements and address evolving market demands. This approach fosters trust and loyalty, contributing to Amkor’s sustained growth and market leadership.
Amkor Technology’s Major Customers and Industry Segments
Amkor’s client list is confidential, protecting the interests of its partners. However, public information indicates that Amkor serves a significant number of major semiconductor companies globally. These clients represent a wide range of industry segments, including but not limited to: consumer electronics (smartphones, tablets, wearables), communications infrastructure (5G networks, data centers), automotive (advanced driver-assistance systems, electric vehicles), and industrial (IoT devices, medical equipment). The breadth of these segments provides Amkor with resilience against market fluctuations in any single sector.
Relationship Dynamics Between Amkor and Key Clients
Amkor’s relationships with its key clients are characterized by a high degree of collaboration and mutual dependence. Amkor’s expertise in advanced packaging and testing is crucial for its clients’ ability to manufacture and deliver cutting-edge products. In return, Amkor benefits from the ongoing demand for its services, ensuring a stable revenue stream and opportunities for growth. This synergistic relationship reinforces Amkor’s position as a trusted partner within the semiconductor industry. Many partnerships span decades, showcasing the longevity and value of these collaborations.
Factors Influencing Amkor Technology’s Customer Relationships
Several factors significantly influence the dynamics of Amkor’s customer relationships. These include: the quality and reliability of Amkor’s services, the company’s technological leadership in advanced packaging solutions, its ability to meet stringent delivery timelines, its competitive pricing, and its commitment to strong customer service and support. Maintaining a robust and responsive supply chain, ensuring continuous innovation, and adapting to the evolving needs of the semiconductor industry are all vital in fostering and sustaining these important relationships. A commitment to security and data protection is also critical in building and maintaining trust with clients handling sensitive information.
Amkor Technology’s Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Performance
Amkor Technology recognizes the importance of integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into its business strategy. The company actively works to minimize its environmental footprint, foster a responsible and ethical workplace, and maintain robust corporate governance practices. This commitment is reflected in various initiatives and reporting frameworks.
Amkor’s approach to ESG is multifaceted, encompassing environmental sustainability, social responsibility, and strong governance structures. Their efforts aim to create long-term value for stakeholders while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Amkor Technology’s Environmental Sustainability Initiatives
Amkor actively pursues environmental sustainability through several key initiatives. These efforts focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving water and energy, and responsibly managing waste. The company’s commitment extends to its entire value chain, from sourcing materials to end-of-life product management. Specific examples of their programs include investments in energy-efficient equipment, the implementation of water recycling systems, and the reduction of waste through optimized manufacturing processes. They also participate in industry collaborations to advance sustainable practices within the electronics sector. Amkor regularly publishes sustainability reports detailing their progress and targets in these areas. For example, a report might detail a percentage reduction in carbon emissions year-over-year, or a specific target for renewable energy usage by a certain date.
Amkor Technology’s Commitment to Social Responsibility and Ethical Business Practices
Amkor’s commitment to social responsibility extends to its employees, suppliers, and the communities where it operates. The company prioritizes ethical business conduct, fostering a diverse and inclusive workplace, and promoting human rights throughout its supply chain. This includes adherence to strict codes of conduct, robust supplier engagement programs to ensure ethical sourcing, and initiatives aimed at supporting local communities through philanthropic activities or employee volunteer programs. For example, Amkor might detail their employee volunteer hours dedicated to community projects or their efforts to promote diversity and inclusion through specific training programs and recruitment strategies. The company emphasizes transparency and accountability in its social responsibility efforts.
Amkor Technology’s Governance Structure and Corporate Social Responsibility Reports
Amkor Technology operates under a well-defined governance structure, ensuring transparency and accountability in its operations. This includes a Board of Directors overseeing the company’s strategic direction and a robust internal control system to manage risks and ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations. The company regularly publishes Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) reports, providing stakeholders with detailed information on its ESG performance. These reports Artikel Amkor’s goals, progress, and challenges related to environmental sustainability, social responsibility, and governance. The reports often follow globally recognized reporting frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) standards, allowing for consistent benchmarking and comparison with industry peers. These reports are typically available on Amkor’s investor relations website.
Amkor Technology’s Growth Strategy
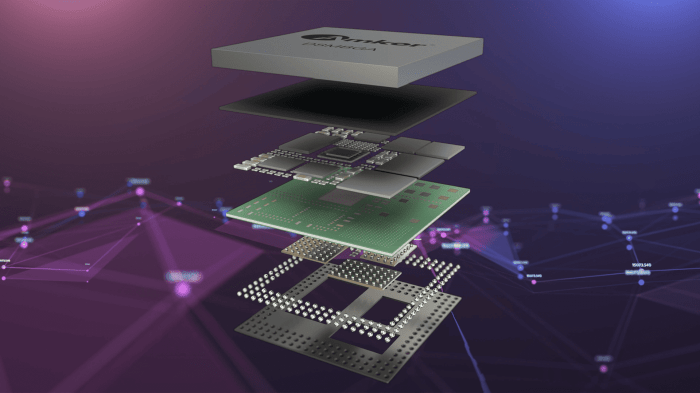
Amkor Technology’s growth strategy centers on leveraging its existing strengths in advanced packaging technologies while strategically expanding into high-growth market segments. This involves a multi-pronged approach focusing on technological innovation, strategic partnerships, and operational efficiency to meet increasing global demand for semiconductor solutions. The company aims to achieve sustainable, profitable growth by capitalizing on industry trends and proactively adapting to evolving customer needs.
Amkor’s strategic priorities are aligned with the overarching goal of becoming the leading provider of outsourced semiconductor packaging and testing services. This involves continuous investment in research and development, expansion into new geographical regions and product categories, and fostering strong relationships with key customers. Growth objectives are primarily focused on increasing market share within existing segments and successfully penetrating new, high-potential markets, such as automotive, 5G infrastructure, and high-performance computing.
Amkor Technology’s Strategic Priorities and Growth Objectives
Amkor’s growth strategy is underpinned by several key priorities. Firstly, the company prioritizes technological leadership through continuous investment in R&D to develop cutting-edge packaging solutions that meet the ever-increasing performance demands of its customers. This includes advancements in areas such as system-in-package (SiP) technology, heterogeneous integration, and advanced packaging materials. Secondly, Amkor focuses on geographic expansion, targeting regions with strong growth potential in the semiconductor industry. This expansion includes both organic growth within existing facilities and strategic acquisitions to increase capacity and market reach. Finally, strengthening customer relationships is paramount, focusing on long-term partnerships and collaborative innovation to ensure Amkor remains a preferred supplier for its customers’ most demanding projects. These priorities are reflected in Amkor’s stated growth objectives, which typically involve a combination of revenue growth targets, margin improvement goals, and expansion into new market segments. For example, Amkor might target a specific percentage increase in revenue year-over-year, while simultaneously aiming to improve its operating margins through increased efficiency and higher-value product offerings.
Expansion into New Markets and Product Segments
Amkor’s expansion strategy involves both organic growth within existing markets and strategic entry into new, high-growth segments. The company is actively pursuing opportunities in the automotive sector, driven by the increasing demand for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and electric vehicles (EVs). This requires adapting its packaging solutions to meet the stringent reliability and safety requirements of the automotive industry. Similarly, Amkor is investing heavily in 5G infrastructure, recognizing the significant growth potential in this area. This involves developing packaging solutions optimized for the high-speed data transmission and low-latency requirements of 5G networks. Another key focus is on high-performance computing (HPC), driven by the growing need for faster and more energy-efficient computing solutions in areas such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Amkor’s expansion into these segments often involves strategic partnerships with leading semiconductor companies to jointly develop and deploy innovative packaging solutions. For instance, collaborations with leading chip manufacturers allow Amkor to gain access to cutting-edge technology and a wider customer base.
Achieving Stated Growth Targets
Amkor’s approach to achieving its growth targets relies on a combination of organic growth initiatives and strategic acquisitions. Organic growth is driven by increasing demand for its existing services, coupled with successful penetration into new market segments. This is supported by investments in capacity expansion, technological advancements, and improvements in operational efficiency. Strategic acquisitions play a crucial role in accelerating growth by providing access to new technologies, customer bases, and geographical markets. Amkor carefully evaluates potential acquisition targets based on strategic fit, technological capabilities, and financial viability. A successful example of this strategy would be the acquisition of a company specializing in a particular packaging technology or serving a specific market segment that aligns with Amkor’s overall growth strategy. By combining organic growth with strategic acquisitions, Amkor aims to achieve a balanced and sustainable growth trajectory. This approach mitigates risk and allows for more agile adaptation to changing market dynamics.
Amkor Technology’s Risks and Challenges
Amkor Technology, like any company in the semiconductor industry, faces a complex web of risks and challenges that could significantly impact its financial performance and long-term sustainability. These risks span across geopolitical factors, market fluctuations, technological advancements, and operational efficiencies. Understanding these risks and the company’s mitigation strategies is crucial for a comprehensive assessment of Amkor’s prospects.
Geopolitical and Macroeconomic Risks
The global semiconductor industry is highly sensitive to geopolitical events and macroeconomic conditions. Trade wars, sanctions, and political instability in key regions can disrupt supply chains, impact demand, and increase operating costs. For example, the US-China trade tensions have created uncertainty and increased costs for companies sourcing materials and manufacturing products across borders. Amkor’s extensive global operations make it particularly vulnerable to these disruptions. The company mitigates this risk through diversification of its manufacturing footprint and strategic sourcing of materials from multiple suppliers across different geographical locations. Furthermore, Amkor actively monitors geopolitical developments and adjusts its strategies accordingly, seeking to maintain operational flexibility.
Competition and Market Volatility
The semiconductor packaging and testing industry is intensely competitive, with numerous established players and emerging competitors. Fluctuations in demand for semiconductors, driven by factors like economic cycles and technological advancements, can lead to pricing pressure and reduced profitability. For instance, a sudden downturn in the smartphone market could directly impact Amkor’s revenue, as smartphones are a significant end-market for its services. Amkor addresses this through continuous innovation, strategic partnerships, and a focus on providing specialized and high-value packaging solutions that differentiate it from competitors. This strategy aims to capture market share in high-growth segments and reduce dependence on cyclical markets.
Technological Disruptions and Innovation, Amkor technology
The semiconductor industry is characterized by rapid technological advancements. Failure to adapt to new technologies and manufacturing processes could render Amkor’s existing capabilities obsolete, impacting its competitiveness. The emergence of advanced packaging technologies, for example, requires substantial investment in research and development and necessitates a skilled workforce capable of mastering these new techniques. Amkor counters this challenge through significant R&D investment, strategic acquisitions of companies with complementary technologies, and collaborations with leading semiconductor manufacturers to stay ahead of the technological curve. This proactive approach aims to ensure Amkor remains at the forefront of packaging innovation.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Material Shortages
The semiconductor industry relies on complex and global supply chains. Disruptions to these supply chains, whether due to natural disasters, pandemics, or geopolitical instability, can severely impact Amkor’s ability to meet customer demand and maintain production schedules. The COVID-19 pandemic, for example, highlighted the vulnerability of global supply chains, causing shortages of key materials and impacting manufacturing output worldwide. Amkor mitigates this risk by diversifying its supplier base, building strategic inventory buffers, and implementing robust risk management protocols to ensure business continuity in the face of unforeseen disruptions. The company also invests in improving its supply chain visibility and responsiveness through advanced technologies and data analytics.
Amkor Technology’s Leadership and Management

Amkor Technology’s success is significantly shaped by its leadership team and the overall management structure. The company’s approach to leadership, organizational structure, and corporate culture all contribute to its operational efficiency and strategic direction. Understanding these aspects provides valuable insight into Amkor’s overall performance and future prospects.
Amkor Technology’s leadership is comprised of experienced professionals with diverse backgrounds in semiconductor manufacturing, business management, and finance. Their collective expertise guides the company’s strategic decisions and operational execution. The company’s organizational structure facilitates efficient communication and collaboration across its global operations. A well-defined management style fosters a productive work environment and encourages innovation.
Key Executives and Their Backgrounds
Amkor Technology’s leadership team includes individuals with extensive experience in the semiconductor industry. While specific titles and individual biographies change over time, a review of Amkor’s investor relations materials and press releases will reveal the current leadership structure and provide detailed backgrounds for each executive. These backgrounds typically include advanced degrees in engineering, business administration, or related fields, along with significant experience in operational management, strategic planning, and financial leadership within the semiconductor or technology sectors. The CEO, for example, usually possesses a proven track record of successfully leading large-scale organizations and navigating complex global markets. Other key executives, such as the CFO and COO, bring specialized expertise in financial management and operational excellence, respectively.
Organizational Structure and Management Style
Amkor Technology employs a hierarchical organizational structure, common in large multinational corporations. This structure typically involves various departments and functional units, each with designated responsibilities and reporting lines. The management style is likely a blend of strategic direction from the top leadership and operational autonomy within individual departments. This balance allows for both centralized control and decentralized decision-making, enabling swift responses to market demands and operational challenges. Effective communication and collaboration are likely emphasized across departments to ensure seamless coordination of activities. Performance metrics and regular reviews likely play a crucial role in evaluating progress and identifying areas for improvement.
Corporate Culture and Employee Relations
Amkor Technology’s corporate culture is likely characterized by a focus on innovation, collaboration, and operational excellence. The company’s commitment to its employees is often highlighted in its public communications. A strong emphasis on employee development and training is likely a key component of their strategy for attracting and retaining talent in a competitive industry. Open communication channels and opportunities for employee feedback are probably encouraged to foster a positive and productive work environment. The company’s commitment to diversity and inclusion is also likely a significant aspect of its corporate culture. Maintaining positive employee relations is vital for Amkor’s continued success in a technologically advanced and competitive global market.
Amkor Technology’s Future Outlook
Amkor Technology’s future prospects are intertwined with the broader trends shaping the semiconductor industry. Continued growth in the demand for advanced packaging solutions, driven by the proliferation of mobile devices, high-performance computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT), presents significant opportunities. However, geopolitical factors, intense competition, and technological disruptions also pose considerable challenges. Analyzing industry forecasts and assessing potential opportunities and threats is crucial for understanding Amkor’s trajectory.
Industry Forecasts Relevant to Amkor Technology’s Operations
The global semiconductor packaging market is projected to experience robust growth in the coming years. Market research firms like Gartner and IDC consistently predict a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 5%, fueled by the increasing complexity and miniaturization of electronic devices. This growth is expected to be particularly strong in advanced packaging technologies, such as system-in-package (SiP) and 3D packaging, areas where Amkor holds a strong position. For example, the rising demand for high-bandwidth memory (HBM) in data centers and artificial intelligence applications is directly beneficial to Amkor’s advanced packaging capabilities. This positive outlook is further reinforced by the ongoing investments in semiconductor manufacturing capacity globally, creating a need for increased packaging services.
Potential Future Opportunities for Amkor Technology
Amkor is well-positioned to capitalize on several key opportunities. Expansion into new markets, such as automotive electronics and medical devices, represents a significant growth avenue. These sectors are experiencing rapid technological advancements and increasing demand for sophisticated packaging solutions. Further development and investment in advanced packaging technologies, such as chiplets and heterogeneous integration, will allow Amkor to maintain a technological edge and attract high-value customers. Strategic partnerships and acquisitions could also accelerate growth and expand Amkor’s capabilities into new geographic regions and technological domains. For instance, a partnership with a leading designer of AI chips could provide Amkor with access to cutting-edge technologies and a large customer base.
Potential Future Threats to Amkor Technology’s Continued Success
Amkor faces several potential threats. Geopolitical instability and trade tensions could disrupt supply chains and impact manufacturing operations. The semiconductor industry is characterized by intense competition, and new entrants and existing players continually strive for market share. Maintaining a competitive edge requires ongoing investment in research and development, as well as efficient manufacturing processes. Fluctuations in demand for semiconductors, particularly in response to economic downturns, could significantly impact Amkor’s revenue and profitability. Finally, technological advancements could render some of Amkor’s existing technologies obsolete, necessitating continuous adaptation and innovation. The rise of new packaging technologies could potentially marginalize Amkor’s current offerings if they fail to adapt and invest in new solutions.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, Amkor Technology’s success hinges on its ability to adapt to the ever-evolving demands of the semiconductor industry. Its robust business model, technological prowess, and strategic partnerships position it for continued growth, though navigating the inherent risks and challenges within the global supply chain remains paramount. Future success will depend on its capacity for innovation, its ability to maintain strong customer relationships, and its commitment to sustainable and ethical business practices.
Amkor Technology, a global leader in semiconductor packaging and test services, relies on a skilled workforce. To cultivate this talent pipeline, collaborations with institutions like the nyc college of technology are crucial for sourcing engineering graduates. These partnerships ensure Amkor maintains access to a steady stream of qualified individuals, contributing to their ongoing success in the competitive tech landscape.
Amkor Technology, a global leader in semiconductor packaging, offers a diverse range of opportunities. For those interested in a rewarding career leveraging technical expertise, exploring options like technology sales jobs could be a great fit. These roles are crucial to Amkor’s success, connecting innovative solutions with clients worldwide and contributing to the company’s continued growth.




